
Introduction: How Much Electricity Does a Hydrogen Generator Really Use?
Hydrogen generator electricity is often the first concern when planning hydrogen production. Users want a clear answer: how much power does a hydrogen generator actually consume, and what does that mean for cost and system design?
In reality, electricity use depends on the hydrogen output, system efficiency, and technology type. In this article, we explain the numbers behind hydrogen generator electricity and how modern electrolysis hydrogen generators fit into today’s green hydrogen generating equipment solutions.
How Much Electricity Does a Hydrogen Generator Use?
A Direct Answer to the Core Question
In theory, producing hydrogen from water requires a minimum amount of electrical energy. Based on thermodynamic limits, generating 1 kg of hydrogen needs at least about 39.4 kWh of electricity.
In real operating conditions, commercial electrolysis systems consume more power. Most hydrogen generators today use:
- 50–55 kWh per kg of hydrogen for standard systems
- Around 45 kWh per kg for high-efficiency systems under optimized conditions
To make this easier to understand, this level of hydrogen generator electricity use is roughly equal to:
- The average electricity consumption of a U.S. household for 1.5 to 2 days
- Enough energy to power a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle for 100–120 km
Why Actual Electricity Use Is Higher Than the Theoretical Value
1.The Physical Limit of Water Electrolysis
Water electrolysis has a fixed physical boundary. The minimum energy required to split water molecules cannot be avoided. This limit defines the lowest possible hydrogen generator electricity consumption.
2.Where Additional Electricity Is Used
In real systems, electricity consumption increases due to several factors:
Electrolysis System Losses
- Overpotential losses caused by electrode reactions
- Electrical resistance inside membranes and components
Balance of Plant Electricity Consumption
- Water purification systems
- Hydrogen drying and purification units
- Cooling systems, pumps, and control units
Power Conversion Losses
- AC to DC conversion typically reaches 95–98% efficiency
- Additional losses occur when renewable power sources are integrated
These combined factors explain why real-world hydrogen generator electricity use exceeds the theoretical minimum.
How Technology Type Affects Hydrogen Generator Electricity
Electrolysis Hydrogen Generator Technologies Compared
Different electrolysis technologies show different electricity consumption levels:
- Alkaline electrolysis (AEL): about 50–60 kWh/kg
- PEM electrolysis: about 45–55 kWh/kg with faster response and higher purity
- SOEC systems: highest theoretical efficiency but limited commercial deployment
Among these, PEM-based electrolysis hydrogen generators are widely used in small and medium-scale applications because they balance efficiency, stability, and flexibility.
For a deeper explanation of PEM systems and their applications, you can read our related article:
PEM Hydrogen Generator for Green Hydrogen Projects: How It Works & Applications
Electricity Consumption in Real Hydrogen Production Systems
1.A Simple Calculation Example
You can estimate hydrogen generator electricity use with a simple formula:
Total electricity (kWh) = Hydrogen output (kg) × Energy consumption (kWh/kg)
For example, a system operating at 52 kWh/kg and producing 96 kg of hydrogen per hour will consume about 5,000 kWh of electricity.
2.How Electricity Cost Shapes Hydrogen Cost
Electricity price directly affects hydrogen production cost:
- At $0.05/kWh, electricity cost per kg of hydrogen is about $2.6
- At $0.10/kWh, the cost doubles to $5.2 per kg
This is why hydrogen generator electricity is one of the most critical factors in green hydrogen economics.
To estimate your own project cost, you can use our Hydrogen Cost Calculator page here:
PEM Hydrogen Generators in Green Hydrogen Generating Equipment
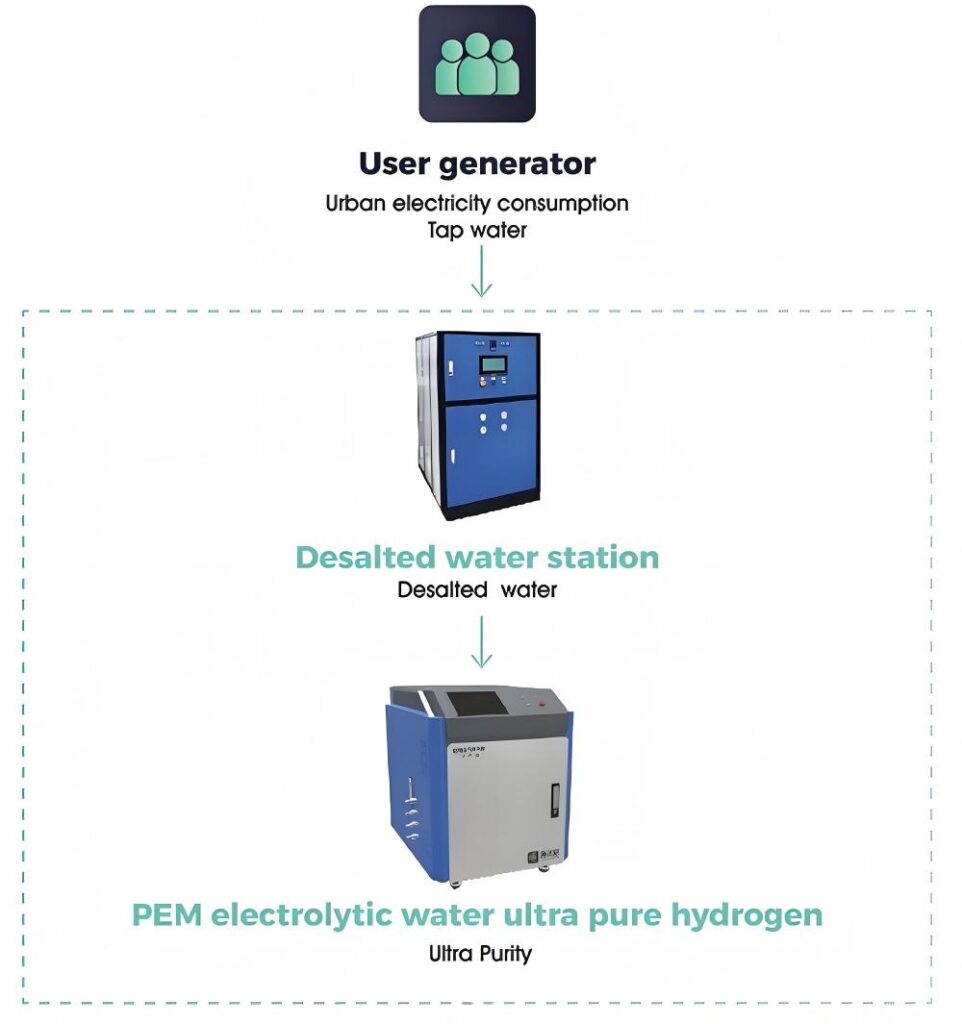
Water Electrolysis Hydrogen Production in Practice
In practical systems, users provide tap water and urban electricity. A desalination station first converts tap water into purified water. This water then enters a PEM electrolyzer, where electricity drives hydrogen production.
The PPH series PEM electrolytic water ultra-pure hydrogen generator produces ultra-pure hydrogen for applications such as thin-film solar cells and semiconductor manufacturing.
HYVODA PPH Series Overview
The PPH series is a small-flow-rate hydrogen generator developed by HYVODA. It uses advanced PEM water electrolysis combined with metal membrane purification. This process delivers hydrogen purity up to 99.9999999%.
Key features include:
- Compact and lightweight design
- One-button start and stop
- Unattended and remote operation
- Low-noise and environmentally friendly performance
These features make the PPH series suitable for laboratories, medical care, and semiconductor facilities.
How to Reduce Hydrogen Generator Electricity Consumption
Several strategies help reduce electricity use:
- Choose high-efficiency electrolysis hydrogen generators
- Operate systems close to rated load for optimal efficiency
- Use renewable electricity during low-price periods
- Improve system integration to reduce auxiliary power losses
With continued material and system optimization, average hydrogen generator electricity consumption is expected to move closer to 40–45 kWh/kg in the future.
Conclusion: What You Should Focus On
In most real projects, producing 1 kg of hydrogen requires about 50–55 kWh of electricity. The exact number depends on technology choice, operating conditions, and system design.
When evaluating green hydrogen generating equipment, users should:
- Treat kWh per kg of hydrogen as a core performance indicator
- Look beyond the electrolyzer itself and consider total system power use
- Pay close attention to local electricity prices and renewable energy availability
FAQs
Q1: Why does hydrogen production use so much electricity?
Because splitting water requires significant energy, and real systems include unavoidable efficiency losses.
Q2: Is PEM technology more energy-efficient?
PEM systems often achieve lower electricity consumption and faster response compared to traditional alkaline systems.
Q3: Can renewable electricity reduce hydrogen cost?
Yes. Lower electricity prices and clean power sources directly reduce hydrogen generator electricity cost.
Q4: What applications benefit most from ultra-pure hydrogen?
Laboratories, medical care, and semiconductor manufacturing benefit the most.
Contact HYVODA
If you are evaluating hydrogen generator electricity consumption or planning a green hydrogen project, HYVODA can support your needs. Our PPH series PEM hydrogen generators provide stable performance, ultra-pure hydrogen, and flexible system integration.
Contact HYVODA today to discuss your application and technical requirements.
