The aerospace industry relies on hydrogen for both propulsion and power generation, as hydrogen offers unmatched efficiency, lightweight energy density, and zero-carbon emissions. From fuel cells to liquid hydrogen propulsion, it plays a vital role in the next generation of sustainable aviation and space exploration.
1. Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cells generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing only water as a byproduct.
They provide aircraft and drones with quiet, efficient, and clean energy, making them ideal for sectors where environmental performance and reliability are crucial.
For example, hydrogen-powered drones achieve flight durations several times longer than those using traditional lithium batteries. Similarly, small passenger aircraft are beginning to adopt hydrogen fuel cells to reduce carbon emissions and improve overall fuel efficiency.
2. Hydrogen Propulsion Systems
Hydrogen propulsion systems use the combustion of hydrogen at high temperatures to generate powerful thrust.
Compared to traditional jet fuels, hydrogen delivers a higher energy density, excellent heat transfer, and virtually zero CO₂ emissions.
In commercial aviation, hydrogen engines can provide sufficient thrust for medium-range aircraft, helping airlines achieve net-zero emission goals.
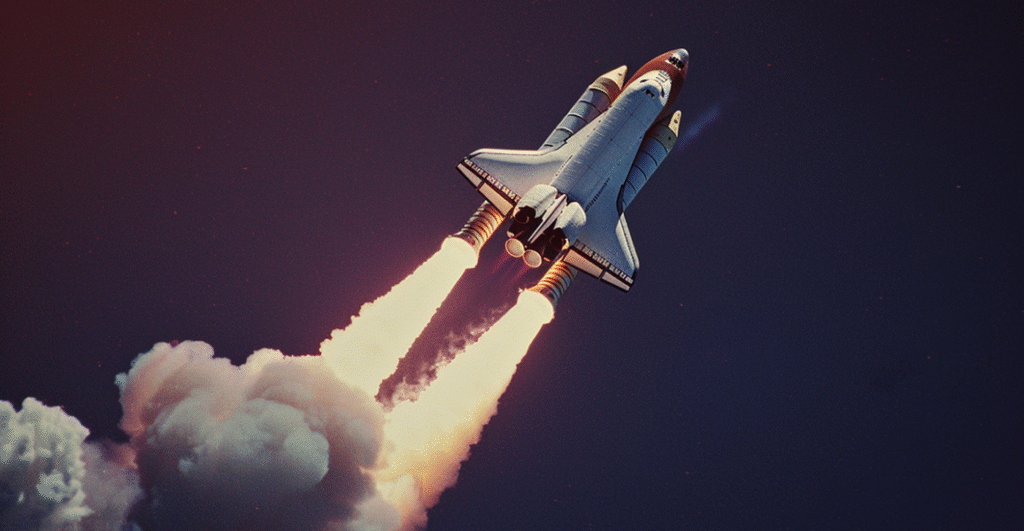
In the space sector, liquid hydrogen combined with liquid oxygen forms one of the most powerful rocket propellants. This combination significantly increases the specific impulse of launch vehicles, improving payload capacity and mission efficiency.
For instance, liquid hydrogen rocket engines have been successfully used in launch vehicles and space shuttles for decades.
3. Hydrogen Quality Requirements
Hydrogen used in aerospace applications must meet strict quality and safety standards to ensure stable performance and flight reliability:
- Purity: Minimum 99.99%, ensuring efficient combustion in fuel cells or propulsion systems.
- Impurities: Oxygen content <10 ppm; CO₂ and SO₂ must remain below defined limits to prevent system damage.
- Temperature: Must meet liquid hydrogen storage requirements to maintain stability and safety.
- Volume Coefficient: Around 0.7 MPa/m³ for stable liquid storage.
- Stability: Hydrogen must remain chemically stable during long-term storage and use.
- Surface Activity: Minimal to prevent degradation when in contact with other materials.
- Radiation Level: Must remain within safe limits to protect personnel and onboard electronics.
4. Reliable Hydrogen Solutions for the Aerospace Industry
HYVODA provides advanced industrial hydrogen production solutions designed for high-purity and high-demand sectors such as the aerospace industry.
Our systems ensure consistent purity, safety, and performance for research institutions and aviation manufacturers.
To discuss your aerospace hydrogen project or request a customized solution, please contact HYVODA.
